Kim Knott
Projects
Articles
Academic Publications
Applying the Study of Religions in the Security Domain: Knowledge, Skills, and Collaboration
Since the 1990s, scholars of religion on both sides of the Atlantic have been drawn into engagement with law enforcement agencies and security policymakers and practitioners, particularly for their expertise on new religious movements and Islam. Whilst enabling researchers to contribute to real-world challenges, this relationship has had its frustrations and difficulties, as well as its benefits and opportunities. Drawing on examples from the UK, Canada, and the US, I set out the relationship between religion and the contemporary security landscape before discussing some of the key issues arising in security research partnerships. I then turn to the question of knowledge exchange and translation in the study of religions, developing the distinction between ‘know what’ (knowledge about religions and being religiously literate), ‘know why’ (explaining religions and making the link to security threats), and ‘know how’ (researcher expertise and skills in engagement with practitioners).
(From the journal abstract)
Kim Knott. 2018. ‘Applying the Study of Religions in the Security Domain: Knowledge, Skills, and Collaboration’. Journal of Religious and Political Practice, 4 (3): 354–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/20566093.2018.1525901.
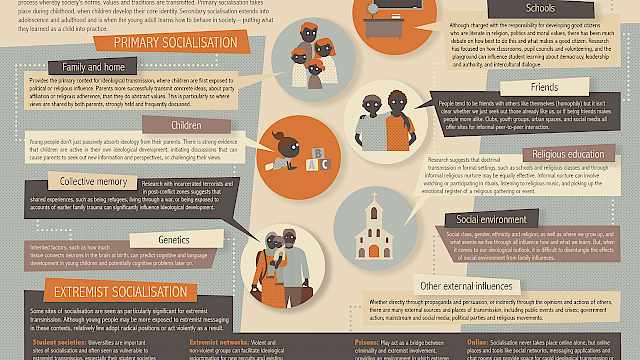
Ideological Transmission in Extremist Contexts: Towards a Framework of How Ideas Are Shared
Despite their centrality in academic and policy debates about radicalization and political violence, ideologies have been conceived narrowly, as cognitive, top-down, coherent and systematic.
In general, those who have used the concept of ideology have failed to draw on ideological theory or on recent insights about its practice and embodiment, or location in space and time.
Our interest is less in the content of ideology than in how it is shared by those for whom it matters. We offer an interpretive framework, based on six key questions about ideological transmission: What ideas, beliefs, and values are shared, how and why, by whom, and in which spatial and temporary contexts?
Following a discussion about the methodological pros and cons of the framework, it is tested on a series of interviews with members of Aum Shinrikyo, the Japanese religious group responsible for the Tokyo subway attack in 1995. We assess the strengths and limitations of the framework for analysing the various dimensions of ideological transmission before considering what it adds to our understanding of the relationship between extreme beliefs and violent behaviour.
(From the journal abstract)
Benjamin Lee, Kim Knott. (2022) Fascist aspirants: Fascist Forge and ideological learning in the extreme-right online milieu. Behavioral Sciences of Terrorism and Political Aggression 14:3, pages 216-240.
https://doi.org/10.1080/21567689.2020.1732938Tips for Connecting Your Research with the Media
During the Religion and Diversity Project’s 2015 annual team meeting, team members and local journalists came together for a panel on presenting research results to the media. Following the lively discussion, on the basis of our experience of researching and working with the media, we were asked to identify key points for communicating research in the press, on radio and television. Here are our top five tips for media engagement, contextualized by our experiences and professional backgrounds.
(From the journal abstract)
Knott, K., & Lefebvre, S. (2016). Tips for Connecting Your Research with the Media. Bulletin for the Study of Religion, 45(1), 32–34.
https://doi.org/10.1558/bsor.v45i1.29999Fascist aspirants: Fascist Forge and ideological learning in the extreme-right online milieu
Learning in extremist settings is often treated as operational, with little regard to how aspiring participants in extremist settings engage with complex and abstract ideological material. This paper examines learning in the context of the amorphous network of digital channels that compose the extreme-right online milieu. Through an in-depth qualitative analysis, we explore how well the prevailing model of extremist ideological learning (in ‘communities of practice’) accounts for the behaviour of aspiring participants of Fascist Forge, a now-defunct extreme-right web forum. The findings suggest that some of the social aspects of communities of practice have been replicated in the online setting of Fascist Forge. However, for a combination of technical and ideological reasons, the more directed and nurturing aspects of learning have not. Several issues are raised about the role of ideological learning in online communities, notably the open accessibility of extremist material, the lack of ideological control leading to potential mutation and innovation by self-learners, and the role of digital learning in the preparation, shaping and recruitment of individuals for real world organising and activism.
(From the journal abstract)
Lee, B., & Knott, K. (2021). Fascist aspirants: Fascist Forge and ideological learning in the extreme-right online milieu. Behavioral Sciences of Terrorism and Political Aggression, 1–25.
https://doi.org/10.1080/19434472.2020.1850842
Projects
Articles
Academic Publications
Applying the Study of Religions in the Security Domain: Knowledge, Skills, and Collaboration
Since the 1990s, scholars of religion on both sides of the Atlantic have been drawn into engagement with law enforcement agencies and security policymakers and practitioners, particularly for their expertise on new religious movements and Islam. Whilst enabling researchers to contribute to real-world challenges, this relationship has had its frustrations and difficulties, as well as its benefits and opportunities. Drawing on examples from the UK, Canada, and the US, I set out the relationship between religion and the contemporary security landscape before discussing some of the key issues arising in security research partnerships. I then turn to the question of knowledge exchange and translation in the study of religions, developing the distinction between ‘know what’ (knowledge about religions and being religiously literate), ‘know why’ (explaining religions and making the link to security threats), and ‘know how’ (researcher expertise and skills in engagement with practitioners).
(From the journal abstract)
Kim Knott. 2018. ‘Applying the Study of Religions in the Security Domain: Knowledge, Skills, and Collaboration’. Journal of Religious and Political Practice, 4 (3): 354–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/20566093.2018.1525901.
Ideological Transmission in Extremist Contexts: Towards a Framework of How Ideas Are Shared
Despite their centrality in academic and policy debates about radicalization and political violence, ideologies have been conceived narrowly, as cognitive, top-down, coherent and systematic.
In general, those who have used the concept of ideology have failed to draw on ideological theory or on recent insights about its practice and embodiment, or location in space and time.
Our interest is less in the content of ideology than in how it is shared by those for whom it matters. We offer an interpretive framework, based on six key questions about ideological transmission: What ideas, beliefs, and values are shared, how and why, by whom, and in which spatial and temporary contexts?
Following a discussion about the methodological pros and cons of the framework, it is tested on a series of interviews with members of Aum Shinrikyo, the Japanese religious group responsible for the Tokyo subway attack in 1995. We assess the strengths and limitations of the framework for analysing the various dimensions of ideological transmission before considering what it adds to our understanding of the relationship between extreme beliefs and violent behaviour.
(From the journal abstract)
Benjamin Lee, Kim Knott. (2022) Fascist aspirants: Fascist Forge and ideological learning in the extreme-right online milieu. Behavioral Sciences of Terrorism and Political Aggression 14:3, pages 216-240.
Tips for Connecting Your Research with the Media
During the Religion and Diversity Project’s 2015 annual team meeting, team members and local journalists came together for a panel on presenting research results to the media. Following the lively discussion, on the basis of our experience of researching and working with the media, we were asked to identify key points for communicating research in the press, on radio and television. Here are our top five tips for media engagement, contextualized by our experiences and professional backgrounds.
(From the journal abstract)
Knott, K., & Lefebvre, S. (2016). Tips for Connecting Your Research with the Media. Bulletin for the Study of Religion, 45(1), 32–34.
Fascist aspirants: Fascist Forge and ideological learning in the extreme-right online milieu
Learning in extremist settings is often treated as operational, with little regard to how aspiring participants in extremist settings engage with complex and abstract ideological material. This paper examines learning in the context of the amorphous network of digital channels that compose the extreme-right online milieu. Through an in-depth qualitative analysis, we explore how well the prevailing model of extremist ideological learning (in ‘communities of practice’) accounts for the behaviour of aspiring participants of Fascist Forge, a now-defunct extreme-right web forum. The findings suggest that some of the social aspects of communities of practice have been replicated in the online setting of Fascist Forge. However, for a combination of technical and ideological reasons, the more directed and nurturing aspects of learning have not. Several issues are raised about the role of ideological learning in online communities, notably the open accessibility of extremist material, the lack of ideological control leading to potential mutation and innovation by self-learners, and the role of digital learning in the preparation, shaping and recruitment of individuals for real world organising and activism.
(From the journal abstract)
Lee, B., & Knott, K. (2021). Fascist aspirants: Fascist Forge and ideological learning in the extreme-right online milieu. Behavioral Sciences of Terrorism and Political Aggression, 1–25.